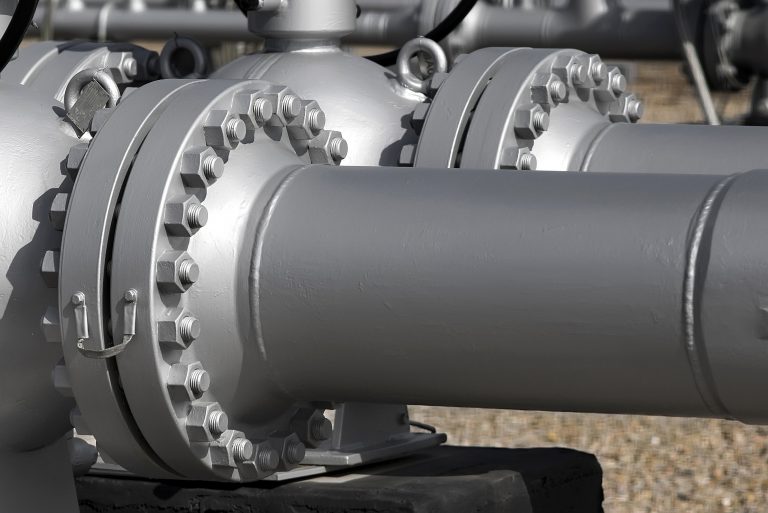
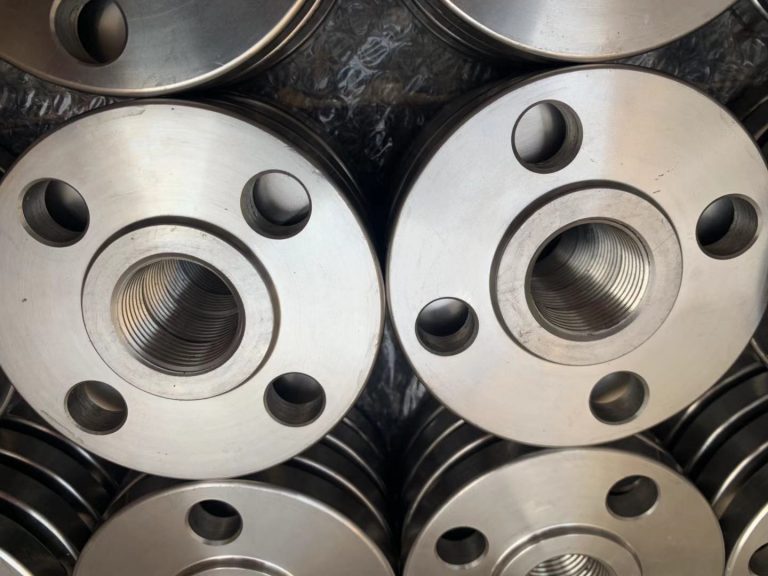
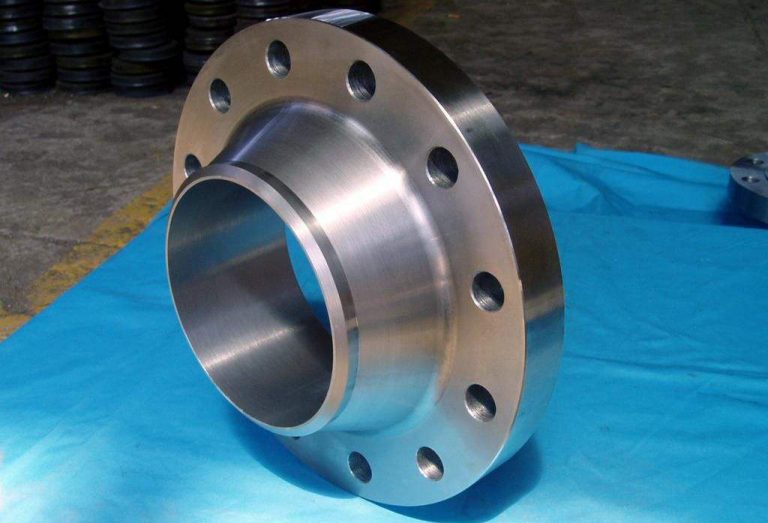
Flanges play an essential role in the seamless functioning of piping systems across various industries. They serve as crucial connectors, ensuring secure and leak-proof joints. The significance of flanges cannot be overstated, as they enable the flow of liquids, gases, and other substances through pipelines with utmost efficiency and reliability. In this blog, we delve into the world of flanges, exploring their definition, purpose, and the industry standards that govern their sizing.
what is a flange?
In engineering and manufacturing, a flange is a projecting flat or raised surface that can be used to connect two pipes or other components, such as valves, pumps, and fittings. Flanges are typically made of metal or plastic, and they come in a variety of shapes and sizes to fit different applications.
Flanges are usually bolted or welded onto the components they are connecting. The flat surface of the flange provides a large area for the bolts or welds to grip onto, creating a strong and secure connection that can withstand high pressure, high temperature, and other stresses.
Flanges are commonly used in a variety of industries, such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment. They are an essential component of many piping systems and play a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient transfer of fluids and gases.
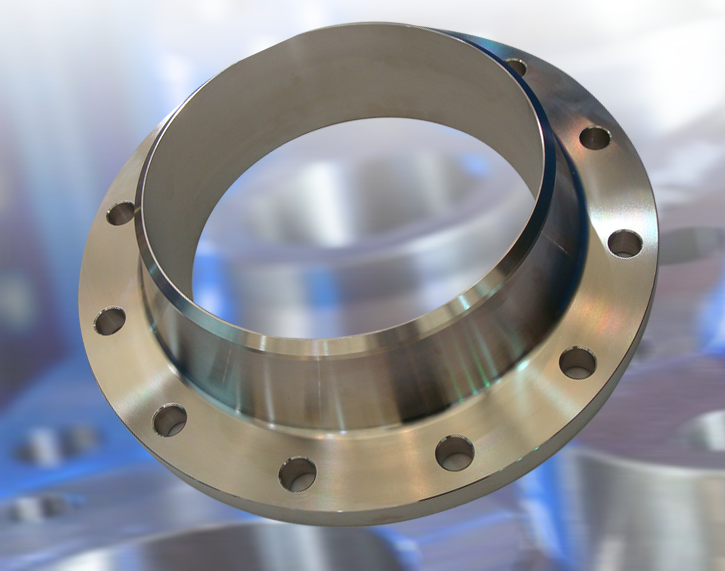

A pipe flange is a disc or collar that is used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment to form a piping system. Flanges are typically made of a material that is compatible with the pipe and the medium being transported, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or various alloys.
Pipe flanges are designed to provide a secure and leak-proof connection between two pipes. They are typically attached to the pipe by welding or threading and are bolted together with another flange to create a connection between the two pipes.
In addition to connecting pipes, flanges can also be used to connect other equipment, such as valves, pumps, and filters, to a piping system. They are widely used in many industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and power generation.
History of Pipe Flanges
Pipe flanges are an essential component of piping systems, used to connect pipes, valves, and other equipment. The history of pipe flanges dates back to the early 19th century when cast iron flanges were used in steam engines and early industrial machinery.
During the Industrial Revolution, as industrialization spread and the demand for steam power increased, the need for efficient and reliable piping systems became evident. Flanges proved to be a vital component in achieving this, as they provided a secure connection between pipes, allowing for the easy assembly and disassembly of piping systems.
In the early 1900s, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) developed industry standards for pipe flanges, ensuring their compatibility and reliability. These standards laid the foundation for the widespread adoption and use of flanges in various industries.

Over the years, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques have further improved the design and performance of flanges. Different types of flanges, such as weld neck, slip-on, threaded, and blind flanges, have been developed to cater to specific needs and applications.
Over time, different materials and designs for pipe flanges were developed to meet various industry needs. For example, weld neck flanges were introduced in the mid-20th century for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, and lap joint flanges were developed for use with stub end fittings.
Today, pipe flanges are used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, water treatment, and more. They continue to play a crucial role in connecting pipes, providing a leak-proof seal, and facilitating the efficient flow of liquids, gases, and other substances in complex piping systems.
Type of flanges
There are several types of flanges used in different applications. Here are some common types:
- Weld Neck Flange (WN): This type of flange has a long neck and allows for easy alignment and welding to the pipe. It is designed to withstand high-pressure applications and is commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation.
- Slip-On Flange (SO): Slip-on flanges are easy to install and require less welding. They slide over the pipe and are then welded in place. They are commonly used in low-pressure and non-critical applications.
- Blind Flange (BL): Blind flanges are used to close the end of a pipe or vessel. They are commonly used in systems that require periodic closure or where inspection and maintenance access is required.
- Threaded Flange: Threaded flanges have internal threads that allow for connection to pipes with external threads. They are commonly used in low-pressure applications and smaller pipe sizes.
- Socket Weld Flange: Socket weld flanges have a socket-like recess where the end of the pipe is inserted and welded for a secure connection. They are commonly used in small-bore piping systems and high-pressure applications.
- Lap Joint Flange (LJ): Lap joint flanges consist of two components – a stub end and a backing flange. The stub end is welded to the pipe, and the backing flange is used to align and bolt the flange joint together. They are commonly used in systems that require frequent assembly and disassembly.
- Orifice Flange (OF): Orifice flanges are used in systems that require the measurement or control of fluid flow. They have additional bolt holes and are designed to accommodate orifice plates or other flow measurement devices.
- Spectacle Blind Flange: Spectacle blind flanges consist of two metal discs connected by a section of pipe. They can be rotated to either block the flow or allow flow through the pipe. They are commonly used in systems that require periodic isolation or flow diversion.
Flanges come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and types, including slip-on flanges, weld neck flanges, socket weld flanges, threaded flanges, and lap joint flanges. Each type of flange is designed for specific applications and has unique features, such as increased strength, easier installation, or greater flexibility.
To learn more about flange types please click: What are different types of flanges?

Pipe flanges materials
Today, pipe flanges are available in a wide range of materials, including carbon steel flanges, stainless steel flanges, and various alloy steel flanges, and are designed for specific applications and industries. They are used in a variety of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and power generation.
Here are some commonly used materials for pipe flanges:
- Carbon Steel: Carbon steel flanges are widely used due to their affordability, strength, and versatility. They are suitable for most general-purpose applications and can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel flanges are highly corrosion-resistant and are often preferred for applications involving corrosive fluids or environments. They offer excellent durability and can withstand high temperatures.
- Alloy Steel: Alloy steel flanges are used when higher strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and tear are required. These flanges are commonly utilized in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron flanges are known for their durability, affordability, and resistance to corrosion. They are commonly used in low-pressure applications, such as in water and sewage systems.
- Brass and Bronze: Brass and bronze flanges are preferred for applications involving lower temperatures and pressures. They offer good corrosion resistance and are often used in plumbing systems and marine applications.
- PVC and CPVC: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) flanges are used in applications where corrosion resistance and chemical compatibility are necessary. These materials are commonly found in water treatment plants, chemical processing, and irrigation systems.
- Titanium: Titanium flanges are utilized in applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in industries such as chemical processing, desalination plants, and aerospace.
Industry standard for flanges
There are several industry standards that specify the dimensions, materials, and testing requirements for flanges. Here are some of the most commonly used standards for flanges:
- ASME B16.5: This standard, published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), covers pipe flanges and flanged fittings from NPS 1/2″ to NPS 24″. It provides dimensions, pressures, and tolerances for flanges made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel.
- ASME B16.47: Also published by ASME, this standard covers larger diameter flanges, typically above NPS 26″. It includes two different series – Series A (MSS SP-44) and Series B (API 605). Series A flanges are typically used for general-purpose applications, while Series B flanges are commonly used in the oil and gas industry.
- DIN EN 1092: This European standard provides requirements for flanges and their joints. It covers a wide range of flange sizes and pressure ratings and specifies materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and non-ferrous metals.
- JIS B2220: This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies the dimensions, materials, and pressure ratings for Japanese flanges. It covers a variety of flange sizes and is commonly used in industries within Japan and countries that adhere to JIS standards.
- BS 4504: This British Standard specifies the dimensions and pressure-temperature ratings for British flanges. It covers a range of flange sizes and materials and is widely used in the United Kingdom and other regions that follow British standards.
The use of pipe flanges

The use of pipe flanges is widespread in various industries and applications due to their versatility and reliability. Here are some common uses of pipe flanges:
- Connecting Pipes: Flanges are primarily used to connect pipes, enabling the easy assembly and disassembly of piping systems. They provide a secure and leak-proof connection, allowing for the efficient and safe flow of liquids, gases, and other substances.
- Pipe Connections and Joints: Flanges are used to join pipes with different diameters or materials. They allow for a smooth transition between different pipe sections, ensuring a continuous flow without disruption or leakage.
- Maintenance and Repair: Flanges facilitate the straightforward maintenance and repair of piping systems. When a section of the pipe needs to be replaced or repaired, flanges allow for easy disconnection and reconnection without disturbing the entire system.
- Accessibility for Inspection: Flanges provide access points for inspection and monitoring of the piping system. By using blind flanges or spectacle blinds, sections of the pipe can be closed off for inspection, allowing for the detection of any issues or potential leaks.
- Pressure Relief: Flanges can be utilized as pressure relief points in piping systems. By incorporating pressure relief valves or rupture discs, excess pressure can be released through the flange, preventing damage to the system and ensuring safety.
- Expansion and Contraction: Flanges accommodate the expansion and contraction of pipes due to temperature changes. By using flexible expansion joints or welding slip-on flanges to compensate for thermal expansion, stress on the system is reduced, minimizing the risk of damage or breakage.
- Equipment Attachment: Flanges provide a means to attach equipment, such as pumps, valves, or instrumentation, to the piping system. This allows for easy installation, replacement, or removal of equipment without disrupting the entire system.
- Customization and Adaptability: Flanges can be customized to meet specific requirements, They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and types, and are designed to meet specific application requirements such, as special materials, sizes, or flange-face configurations. This adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, water treatment, HVAC systems, and more.
Pipe flanges are used in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, power generation, and many others. Overall, pipe flanges play a critical role in the efficient and reliable operation of piping systems in various industries. Their use ensures secure connections, easy maintenance, and adaptability to meet the specific needs of different applications.
Lewis Liu
Hello, I am Lewis Liu, a professional sales engineer with over ten years of experience in the flange fittings industry. I am highly knowledgeable in flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the best solutions to ensure their pipeline systems run smoothly, safely, and reliably.
If you have any questions or concerns regarding flange fittings for your pipelines, whether it’s about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or any other aspect, please feel free to contact me at any time. I am committed to offering professional advice and assistance to help you make informed decisions and meet your needs.





