How do I attach the pipe to the flange?
In this blog post, we will go over the subtleties of fitting pipe to flange, including step-by-step directions and professional advice. At YANHAO, we recognize the value of effective pipe-to-flange connections, and we hope to share our knowledge in this guide to ensure a flawless fit.
Continue reading to learn the best procedures for creating a sturdy and dependable pipe-to-flange connection.
Understanding Pipe to Flange Connections

The purpose of pipe-to-flange connections
The fundamental objective of pipe-to-flange connections is to firmly unite pipes to flanges and create a leak-proof union. These connections are extremely important in many industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, power production, and plumbing. These businesses require pipe-to-flange connections for a variety of reasons, including:
Validate the kind of flanges before installation
There are various types of flange. Before installing pipes and flanges, make sure you understand the sort of flange you’re installing. Let’s talk about some of the most common ones:

Weld Neck Flanges (WN)
WN flange, also known as a trapped hub flange or high-hub flange, is a high-stress-containing flange. Its circular fitting component, the rim, is fitted around the circumference.
China welding neck flange products >>
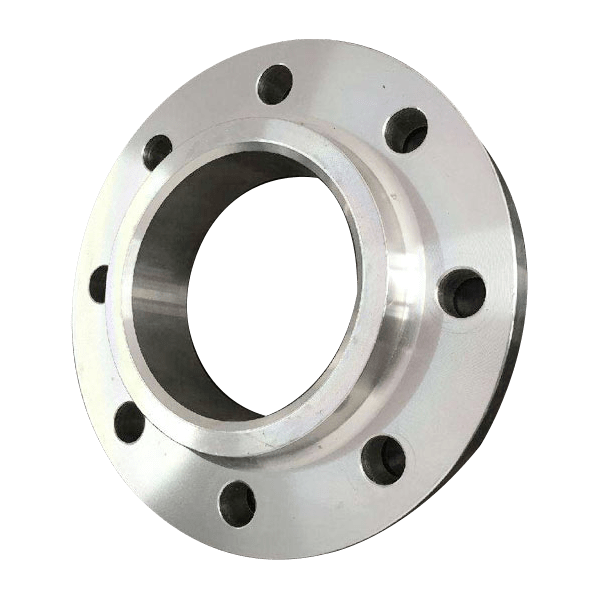

Slip-on Flanges (SO)
Slip-on flanges, as the name shows, can be easily slipped onto the end of a pipe or fitting and then welded in place. It usually has a flat face and a protruding face.
China slip-on flange products >>

Socket Weld Flanges (SW)
Socket Weld Flanges (SW) are similar to Slip-on Flanges (SO). The difference is that there is an extra piece in the middle.
China socket weld flange products >>

Blind Flanges (BF)
Blind flange is also called flange cover. It is a flat, circular plate used to cover the ends of pipes, valves, or joints.
China blind flange products >>
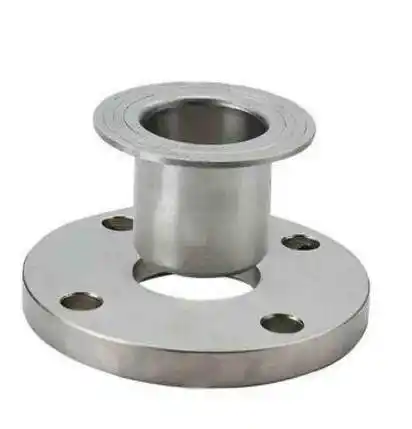

Lap joint flange (LJ)
Consisting of two components: a stub end and a lap joint ring flange. The respective stub end is slid into the flange’s bore, and the stub end is joined to the pipe through butt welding.
China lap joint flange products >>
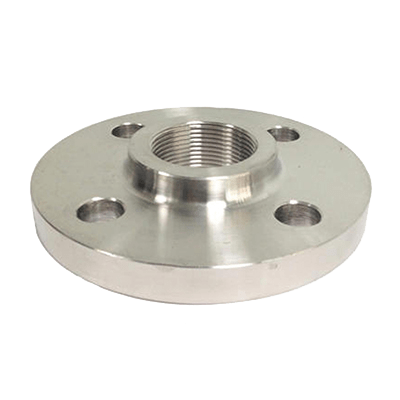

Threaded Flanges (TF)
Threaded flanges are pipe flanges with internal threading to match external threads on a pipe. The installation does not involve welding
China threaded flange products >>
System requirements, pressure ratings, temperature, and climatic conditions all affect the choice of flange because each type has unique advantages and applications.
Essential Tools and Materials for Fitting Pipe to Flange
To properly connect a pipe to a flange, numerous tools and materials are required.

Tools like:

Materials like:
These may also be necessary for the fit-up procedure, depending on the project specifications.
Inspecting and Preparing the Pipe and Flange
Before beginning the fit-up procedure, the pipe and flange must be properly inspected and prepared to ensure a successful and secure connection. Here’s why it matters:
Taking the time to thoroughly inspect and prepare the components prior to the fit-up procedure assures a dependable and long-lasting pipe-to-flange connection.
Step-by-Step Fit-Up Process

Step 1: Accurately Measure and Mark the Pipe for Fit-Up:
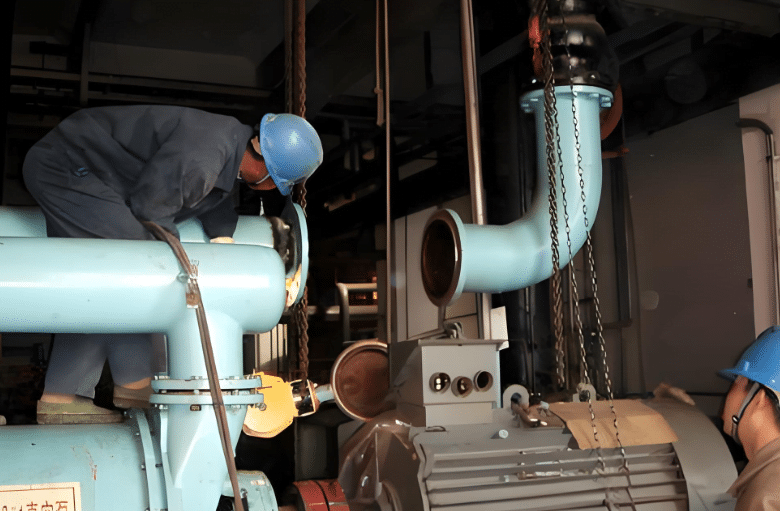
Step 2: Aligning the Pipe and Flange correctly
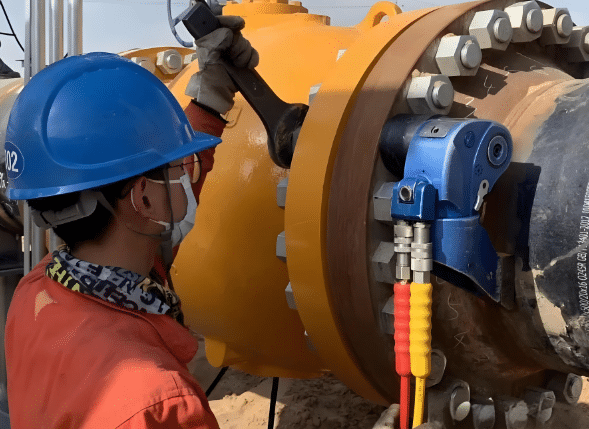

Step 3: Tightening
The particular torque numbers and tightening techniques may differ depending on the project specifications and industry standards. When in doubt, always refer to the recommendations offered and seek advice from YANHAO.
Overcoming Common Challenges of the Fit-Up Process
These solutions should help address common fit-up challenges. However, it is essential to consider specific project requirements, follow industry guidelines, and consult with experienced personnel to ensure a successful fit-up process.
Final
Mastering pipe and flange connection techniques requires expertise, precision, and attention to detail. In this blog post, we explore the necessary steps and expert tips for achieving safe and reliable pipe and flange connections.
At YANHAO, we focus on providing high-quality pipe fitting products, and we believe that by following our comprehensive guidelines, you will be able to achieve excellent results. For all your pipe fitting needs, trust YANHAO, your preferred solution provider.
Author: Lewis Liu
Hello, my name is Lewis Liu, and I’m a professional sales engineer with over a decade of expertise in the flange fittings sector.
I am quite informed about flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the greatest solutions for keeping their pipeline systems running smoothly, safely, and dependably.
If you have any queries or concerns concerning flange fittings for your pipelines, whether they are about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or anything else, please contact me at any time. I am dedicated to providing expert advice and assistance to help you make educated decisions and reach your objectives.
