What is ANSI Flange And How Does it Works
What is ANSI flange?

ANSI flange is a standard produced by the American National Standard Institute (ANSI) that specifies the appearance, size, and pressure level of flanges. ANSI flanges are those that have been constructed in accordance with ANSI specifications. The widespread use of ANSI flanges is due to their standardization and compatibility, which ensure consistency and interchangeability across many industrial applications.
Because these flanges are available in a number of sizes, pressure levels, and materials to fulfill a wide range of application needs, they are frequently employed throughout industries and applications.
Why is it important to use ANSI standard flanges?
The following factors primarily demonstrate the significance of ANSI flanges:
Because of their standardization, compatibility, broad range of applications, and assurance of quality and performance, ANSI flanges are essential to the industrial sector.
Something you should know
The role and standard setting of ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
ANSI (American National Standards Institute) is a private non-profit organization established on October 18, 1918, responsible for the management and coordination of voluntary standardization and conformity assessment systems. ANSI’s mission is to improve the global competitiveness of American business and the quality of life of the American people by promoting and assisting voluntary and consistent standards and conformity assessment work and maintaining their integrity.
ANSI itself rarely formulates standards, but through the appointed group law and the solicitation of opinions law, it selects standards that are of great significance to the country from the standards formulated and issued by various professional groups, and promotes them to national standards after review, and gives them the ANSI code.
Currently, there are more than 180 standard-setting organizations accredited by ANSI, with a total of 37,000 standards, accounting for 75% of non-governmental standards. A small number of them are approved by ANSI as national standards. Of the 11,000 standards formulated and issued by ANSI, only 1,600 are formulated by it itself.
ANSI’s roles and responsibilities include:
- Coordinate the standardization activities of domestic institutions and groups.
- Review and approve American national standards.
- Represent the United States in international standardization activities.
- Provide standard information consulting services.
- Cooperate with government agencies.
ANSI is headquartered in New York and has more than 250 professional societies, associations, consumer organizations and more than 1,000 companies (including foreign companies) participating. Representatives of federal government agencies participate in their activities in their personal capacity and do not accept government funding. ANSI is the official U.S. representative to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and serves as the official U.S. representative to the International Electrotechnical Commission (TEC) through the U.S. National Committee. In addition, ANSI also represents the United States at the Pacific Area Standards Conference (PASC) and the Pan American Standards Committee (COPANT).
Common types of ANSI standard flanges
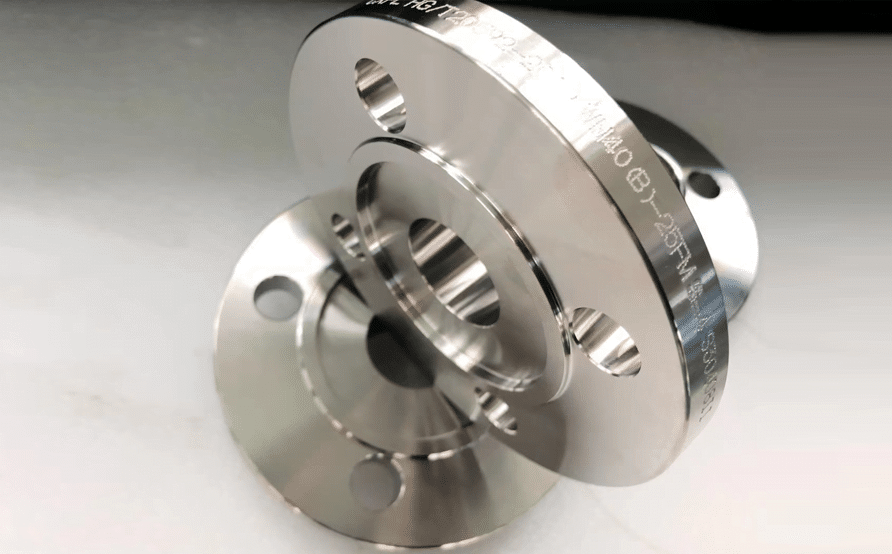

This is the most widely used ANSI flange standard, with widths ranging from NPS 1/2 to NPS 24 with pressure ratings of 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500. This standard specifies the size, material, tolerance, labeling, testing technique, and nomenclature for flange holes.
It comprises a variety of flanges such as butt welding necks, socket welding, threaded connections, loose sleeves, butt welding, and flange covers.
B16 – Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 through NPS 24, Metric/Inch Standard

This standard specifies the dimensions, materials, and testing requirements for large steel flanges ranging in nominal diameter from NPS 26 to NPS 60.
It is separated into two series: flanges with elevated faces (Series A) and flanges with flat faces (Series B).
B16 – Large Diameter Steel Flanges: NPS 26 through NPS 60, Metric/Inch Standard
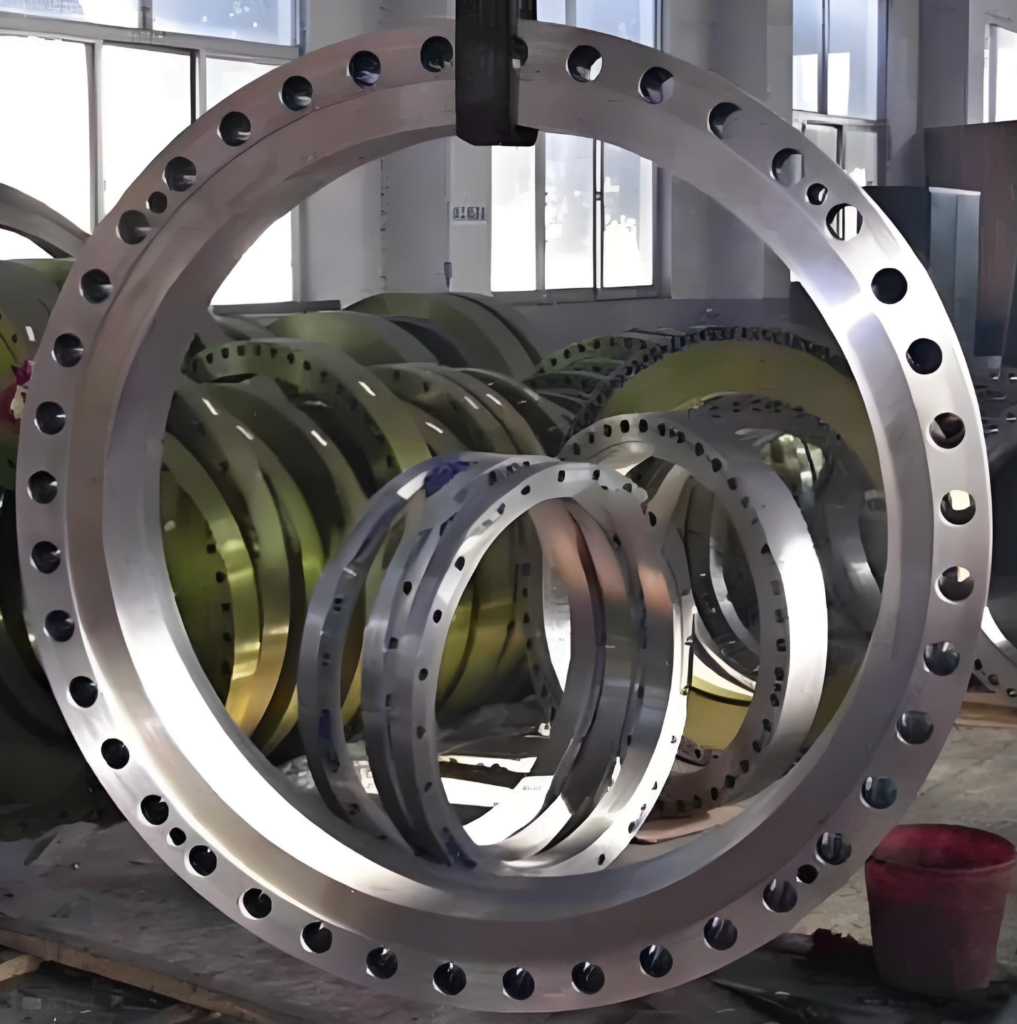

ANSI/MSS SP-44
This standard is specialized to steel pipeline flanges, with sizes ranging from NPS 12 to NPS 60 and pressure levels of 150, 300, 400, 600, and 900.
It defines the pressure-temperature rating, materials, dimensions, tolerances, marking, and testing standards for flanges.
Weld neck flanges must be constructed of forged steel, whereas blind flanges can be made of forged steel or steel plates.
How do we classify flanges?
ANSI flanges can be classified according to pressure level, material, connection method, etc., for example:
- Classification by connection method: welded flange, threaded flange, butt welding flange, etc.
- Classification by material: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc.
- Classification by pressure level: 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500#, etc.
On our website, we have classified flanges in the following categories to help customers choose the right products. To view the flange products, simply click on any of the following:
| Category | Options |
|---|---|
| Flange Standards | ANSI flange | ASME flange | EN Standard Flange | Custom Type |
| Flange Types | Weld Neck Flanges | Slip-On Flanges | Blind Flanges | Lap Joint Flanges | Socket Weld Flanges | Threaded Flanges |
| Flange Materials | Stainless Steel Flanges | Carbon Steel Flanges | Alloy Steel Flanges |
About YANHAO
YANHAO is a flange manufacturer located in Hebei Province, China. It is one of the few professional flange suppliers in China.
We have many years of experience in flange production and have multiple flange production lines. We have sufficient stock of raw materials, rich inventory, fast delivery, and can ship within three days. At the same time, the price is affordable. You are welcome to consult and purchase!
In addition, we can provide a variety of bespoke flanges and pipe fittings. Customers can give drawings or samples, and our company will produce them to fit your specific requirements.
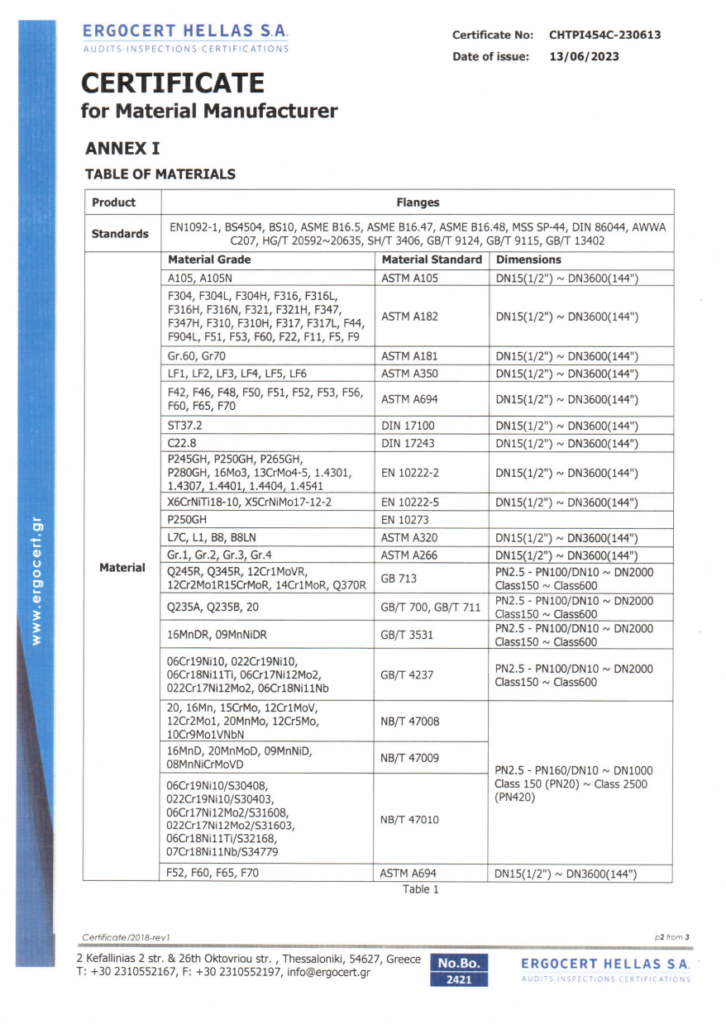
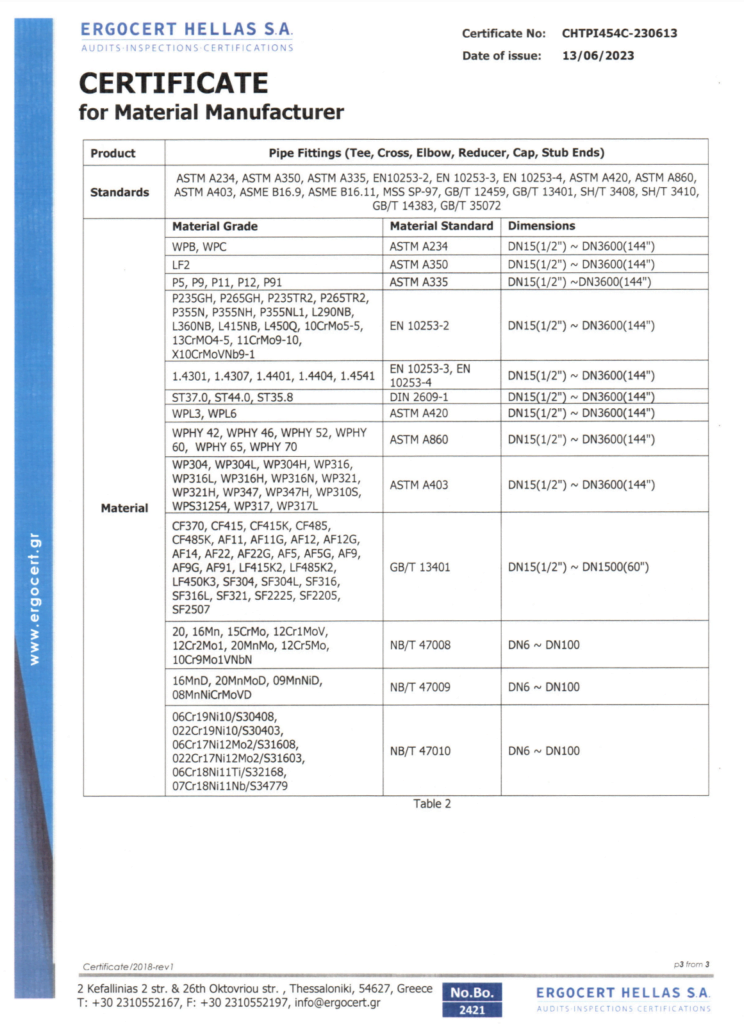
Check Our Certificates
How do we produce ANSI flanges?
At YANHAO, we manufacture flanges in the following steps. Of course, for different user requirements, we will make appropriate adjustments and upgrades to the production process in specific steps. Here, I will only briefly show the production process. If you are interested, you can click to view this article: How a Flange Is Made: The Flange Manufacturing Process.
These steps make up the flange processing process. At YANHAO, we closely monitor and operate each step to ensure that the final product’s quality and performance meet customer expectations.
What are the common application areas of ANSI flanges?
ANSI flanges are widely used in various industrial applications due to their versatility and compatibility. ANSI flanges are available in a variety of sizes, pressure ratings, and materials to meet a variety of application requirements.
I believe that customers who are reading this article will have a basic understanding of the application scenarios of ANSI flanges. I will not go into details here. You can still learn about the specific places where our flanges are used through some of our cooperative customer cases.
Installation and maintenance of ANSI flanges
The installation and maintenance of ANSI flanges is a complex process. There is a set of installation and maintenance standards respectively. I will not elaborate here, but simply list some key points involving safety.
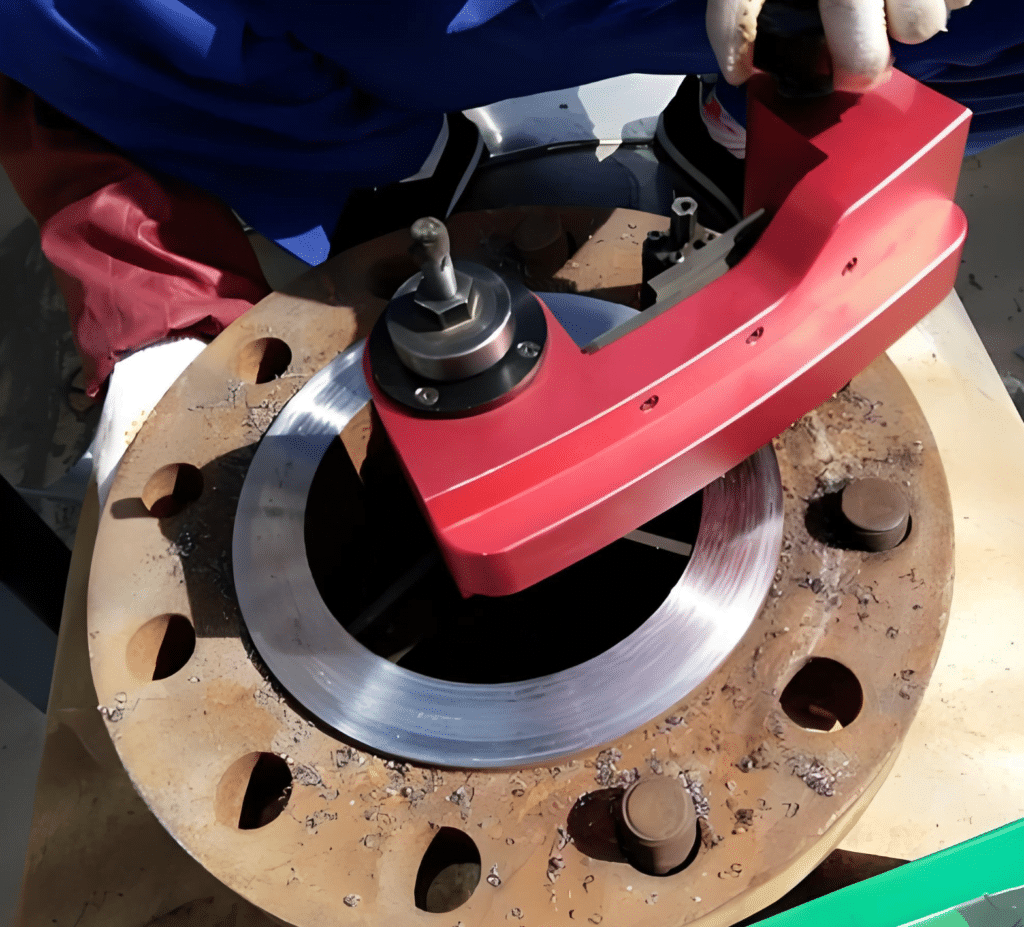
The above are just some simplified precautions, but you can also understand from these that these steps require professional personnel to install and regularly maintain. If you have any questions about this, you can contact YANHAO at any time, and we will arrange professional engineers for guidance.
Recommend Reading:
Finally
The above is everything you need to know about ANSI standard flanges. At YANHAO, we provide various types of ANSI flanges and provide comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales services, such as flange installation guidance, maintenance tutorials, etc. If you need it, please feel free to contact YANHAO.
Author: Lewis Liu
Hello, my name is Lewis Liu, and I’m a professional sales engineer with over a decade of expertise in the flange fittings sector.
I am quite informed about flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the greatest solutions for keeping their pipeline systems running smoothly, safely, and dependably.
If you have any queries or concerns concerning flange fittings for your pipelines, whether they are about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or anything else, please contact me at any time. I am dedicated to providing expert advice and assistance to help you make educated decisions and reach your objectives.